
Modals Can, May, Must, Shall, Will, Ought to, Need, Be to, Have to, Would, Should, … English
NOTE: The term "modal verbs" can be used in different ways.Used as a syntaxic category, it only refers to the single-word verbs can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.Used as a semantic category, it includes the single word modals plus other verbs which express modality in the same way. For students and learners, modality is easier to understand when treated as a semantic.
Difference Between Should and Ought To Meaning, Usage with Examples
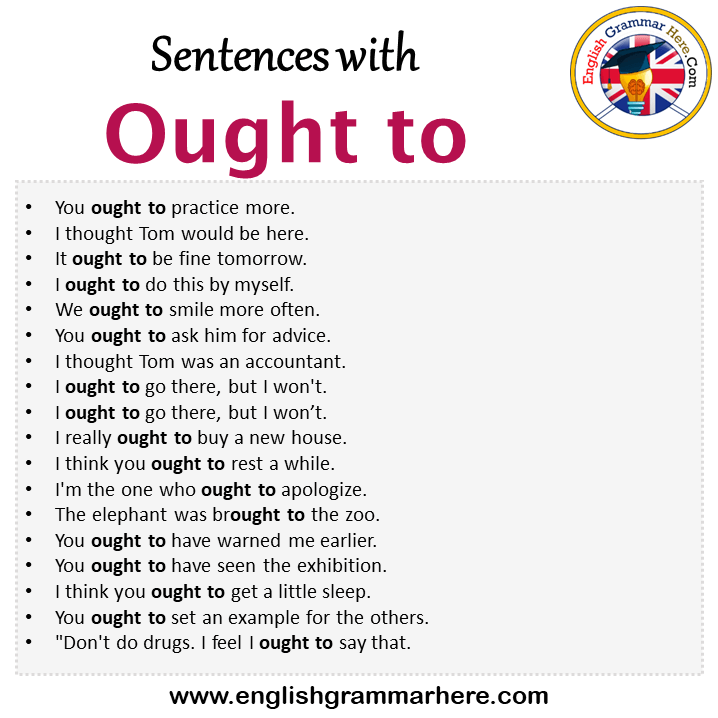
The use of ought to is similar to should, but it is much less frequent. Like should, the verb ought to does not have a past form. It is only used with reference to the present and the future. Ought to is rarely used in questions and negatives. When it is, it is confined mainly to formal styles. In negatives, not comes between ought and to.

Conoce la diferencia entre should, had better, must, have to y ought to Profe Kyle Profe Kyle
How to use should and ought to for strong probability. Substitute the phrase underlined for the should / shouldn't or ought to / oughtn't to structures (both modals are possible in all answers even though there may be small differences in meaning). You can use the contracted (I'm) form or the complete (I am) form of the verb. Example:

SHOULD HAD BETTER OUGHT TO Verbos Modales Gramática Inglés YouTube
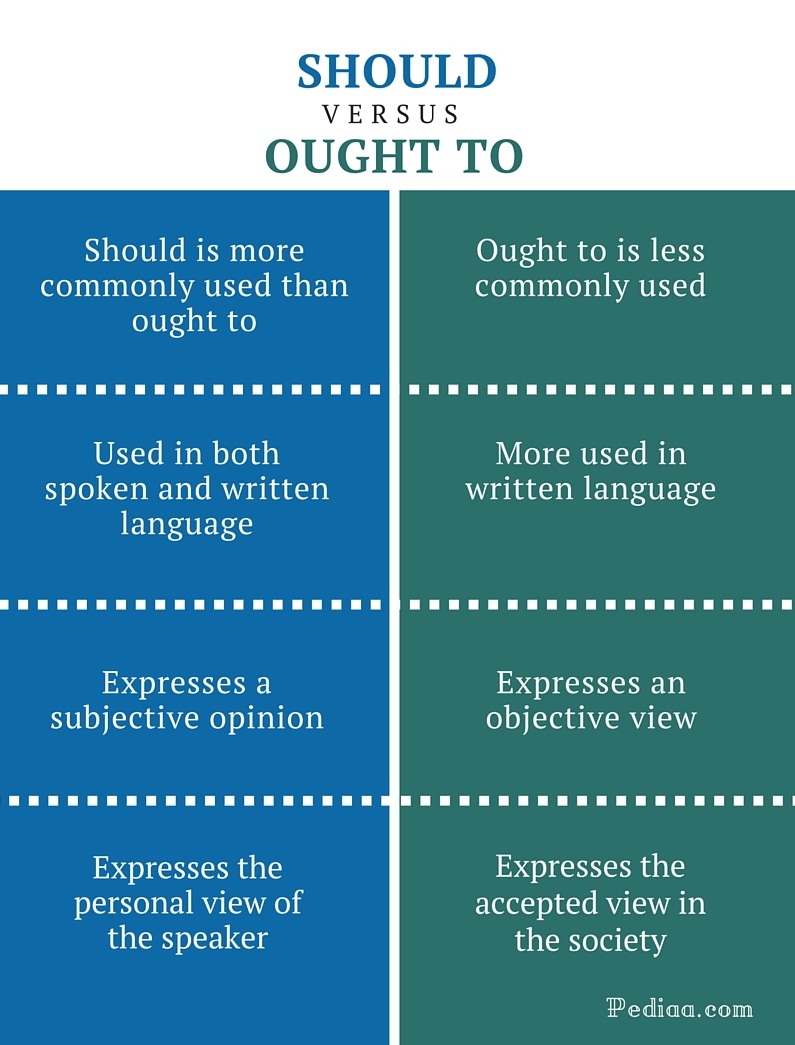
2 181702 SHOULD and OUGHT TO are both modal verbs. Loaded 0% In most cases, SHOULD and OUGHT TO are used interchangeably today. Both SHOULD and OUGHT TO are used to express advice, obligation, or duty. However, there is a slight difference in meaning. SHOULD is used when we want to express our subjective opinion.

Should, ought to, had better gramma… Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
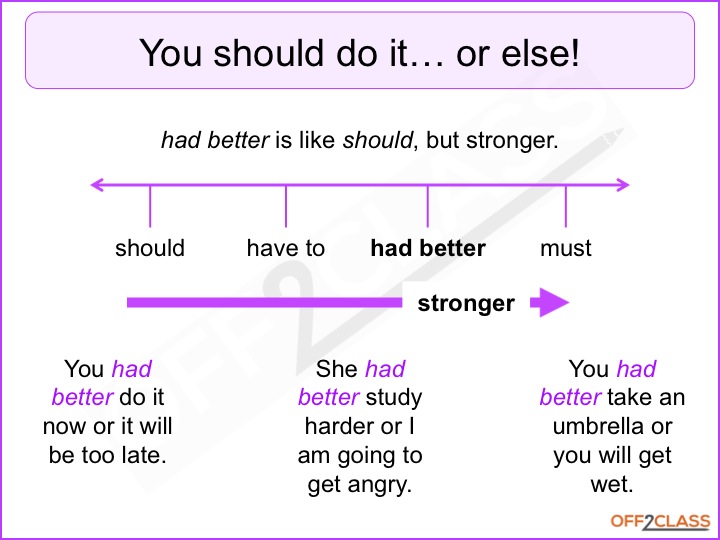
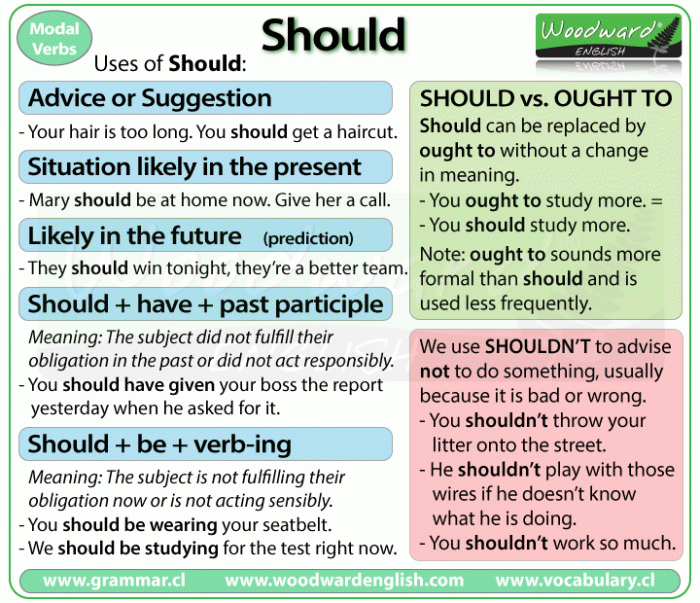
You should go to a therapist. I think schools shouldn't offer soft drinks to their students. Should is not as strong as must or have to. You should be patient with me. (=advice) You must be patient with me. (=strong advice) Ought to/ought not to = should/shouldn't. Ought to has the same meaning as should, although it is more formal and not.

When to use "should/ought to" (an English grammar video) YouTube
'Ought to' is used to express opinions, something which is probable or inform someone about certain necessary duties or obligations. Students often confuse these words and consider them to be synonymous, but they aren't. But both these words can be used interchangeably if one understands the meaning of the sentence they're using these in.

Calaméo Should, ought to, had better
Should and ought to are both modal verbs that express obligation, advice, or recommendation. Should is more commonly used in everyday conversation and should be more formal. While both words express similar meanings, ought to is generally considered more polite and less direct than should and is often used to suggest rather than to demand. Summary

Must or Have to? worksheet Live Worksheets
The negative and interrogative forms of ought to are becoming increasingly rare. Both should and ought to are used to talk about obligation and duty and to give advice. One way of getting the meaning of should across to learners is to contrast its meaning with that of must and have to as the degree of obligation is considerably less, e.g.

Pin de Oleksandr Hreshchuk en Inglès 150 frases en ingles, Modales en ingles, Conversaciones
should What is the difference between should and ought to? 1 expectation You use should or ought to to say that you expect something to happen. We should be there by dinner time. It ought to get easier with practice. You use should or ought to with have and a past participle to say that you expect something to have happened already.

Should & Ought to learnenglish Englisch lernen, Englische grammatik
ENGLISH GRAMMAR MODAL VERBS in English: can, could, may, might, must, mustn't, should, ought to, shall, will Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb which express the mood of another verb. They are used to express ideas such as: possibility, prediction, speculation, deduction and necessity. Modal verbs have the following characteristics:

Modals Should Vs. Ought to
Ought to - should is used to give advice or opinion and one can choose to follow or ignore it, whereas ought to is used when the advice has to be followed. While should and ought to are used interchangeably, ought to is a stronger word compared to should and is more appropriate to use while talking about rules, regulations and laws. Examples -

Should vs Ought to Main verbs, Grammar book, Grammar
Difference between should, ought and must. Must is stronger than should and ought. It is more like an order. Should and ought to, on the other hand, are more like pieces of advice. Compare: He must give up smoking. (=It is an order which is likely to be obeyed.) He should / ought to give up smoking. (= This is more or less a piece of advice.
Should / Ought To / Had Better
Affirmative Ought to comes first in the verb phrase (after the subject and before another verb): We ought to do more exercise. Ought to cannot be used with another modal verb: Medicine ought to be free. Not: Medicine ought to can be free. or Medicine can ought to be free. Negative The negative is formed by adding 'not' after ought (ought not to ).
Should English Modal Verb Uses of Should with Example Sentences Woodward English
3. Margaret ought not stay at home in front of the TV. She should go to the fitness center with us. should : ought to assumption, expectation, probability : 1. She ought to have the package by now. 2. She ought to have received the package yesterday. 3. She ought to receive the package tonight. "Ought not" is used primarily to express negative.
Sentences with There’s, There’s in a Sentence in English, Sentences For There’s English
Complete the sentences. Use the present continuous form of the verb in brackets. Use contractions where possible.

Ought to y Should Uso, Diferencia y Ejemplos [Guía Completa]
Used in the present, future and past. We use 'ought to' to express or ascertain what is correct. You ought not to speak so loudly young lad. I ought to make a trip to the United States one day. I really ought to have seen him yesterday. (past = 'ought to' + present perfect).